当 Quarkus 遇上 LangChain4j
大型语言模型 (LLM) 正在重塑软件世界,改变我们与用户互动和开发业务逻辑的方式。
在 OpenAI 的 ChatGPT 的推广下,LLM 现在有多种类型和规模。Hugging-Face 平台引用了数百个 LLM,Facebook、Google、Microsoft、Amazon 和 IBM 等主要科技公司也提供自己的模型。
LLM 并不是一个新概念。它们已经存在了一段时间,但直到 OpenAI 公开 ChatGPT API 之前,它们并没有像现在这样强大或易于访问。从那时起,Quarkus 团队一直在思考将 LLM 集成到 Quarkus 生态系统中的意义。Lize Raes 在 Devoxx 2023 上的演讲 Java Meets AI 是一个很好的灵感来源。
此后,Quarkus 团队与 Dmytro Liubarskyi 和 LangChain4j 团队合作,开发了一个用于将 LLM 集成到 Quarkus 应用程序中的扩展。该扩展基于 LangChain4j 库,该库提供了一个通用的 API 来与 LLM 进行交互。LangChain4j 项目是著名的 langchain 库的 Java 重写。
在这篇博文中,我们将介绍如何使用刚刚发布的 quarkus-langchain4j 0.1 扩展将 LLM 集成到 Quarkus 应用程序中。此扩展旨在探索 LLM 如何在 Quarkus 应用程序中使用。
我们录制了关于此扩展的现场炉边谈话。您可以在此处观看,博文继续在 下方。
概述
首先,让我们看看全局。将 LLM 集成到 Quarkus 应用程序时,您需要描述 AI 要做什么。与传统代码不同,您将使用自然语言来解释 AI 的行为。当然,有一些技巧可以驯服 AI,但我们稍后会探讨。
仅依赖 LLM 的知识可能不够。因此,Quarkus LangChain4j 扩展提供了两种机制来扩展 AI 的知识:
-
工具 - 工具允许 LLM 在您的应用程序中执行操作。例如,您可以使用工具发送电子邮件、调用 REST 端点或执行数据库查询。LLM 决定何时使用工具、方法参数以及如何处理结果。
-
文档存储 - LLM 不擅长记忆。此外,它们的上下文大小有限。因此,该扩展提供了一种从文档存储中存储和检索信息的方法。在调用 LLM 之前,该扩展可以从文档存储中请求相关文档并将其附加到上下文中。然后,LLM 可以使用这些数据来做出决策。例如,您可以加载电子表格数据、报告或数据库中的数据。
下图说明了 LLM、工具和文档存储之间的交互。
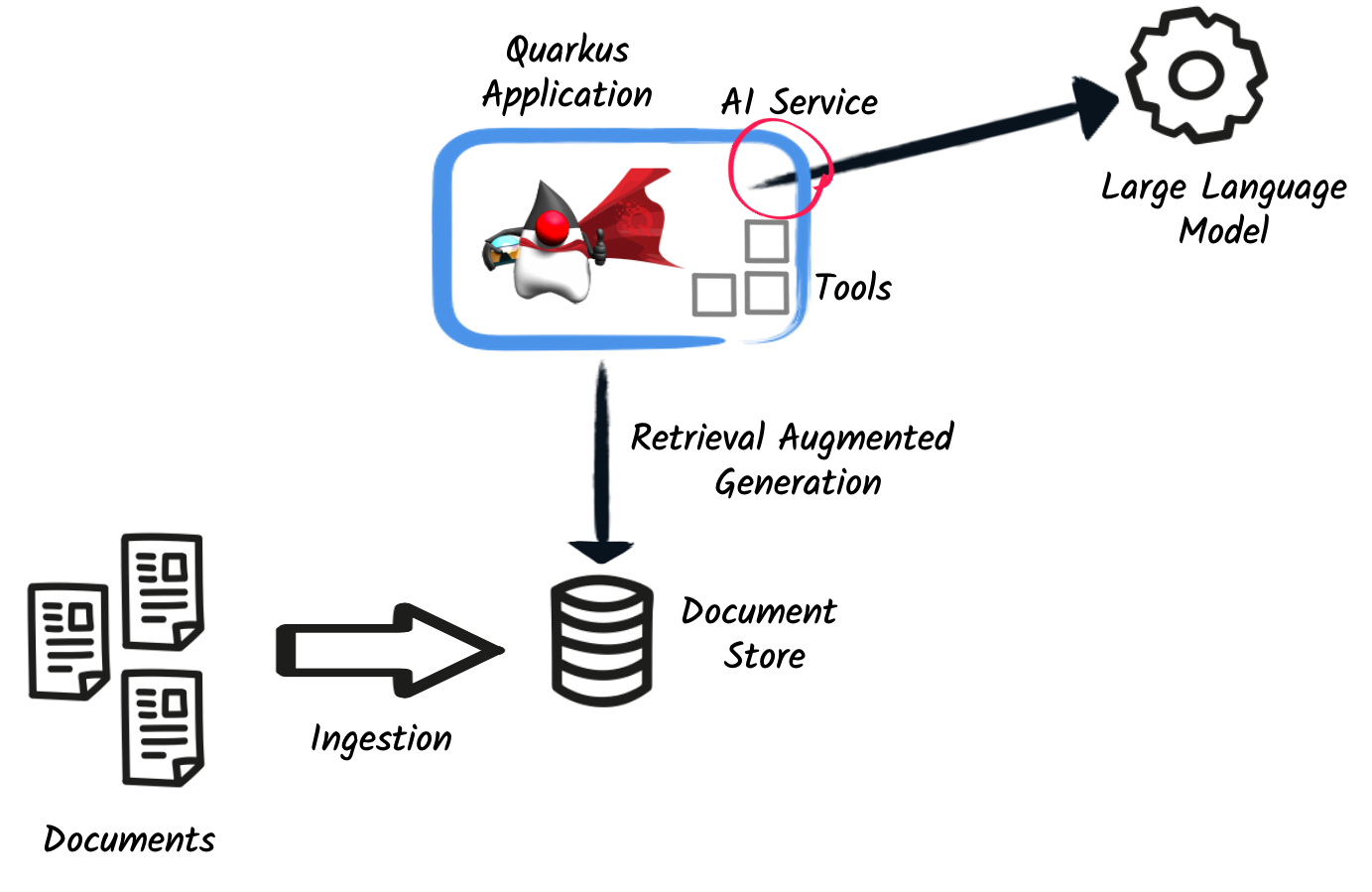
给我看些代码!
好了,废话少说,让我们看些代码!我们将使用 Open AI GPT-3.5(请注意,它不是最先进的模型,但足以用于本次演示),给它一些产品评论,并要求 LLM 将它们分类为正面和负面评论。完整的代码可在 quarkus-langchain4j 存储库 中找到。
首先,我们需要 quarkus-langchain4j-openai 扩展。
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkiverse.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-langchain4j-openai</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version> <!-- Update to use the latest version -->
</dependency>有了扩展后,就该告诉 LLM 我们想要做什么了。Quarkus LangChain4J 扩展提供了一种声明式的方式来描述 LLM 交互。理念与 Quarkus REST 客户端相同。我们使用带有 @RegisterAiService 注释的接口来建模交互。
@RegisterAiService
public interface TriageService {
// methods.
}应用程序的其余部分可以通过注入 TriageService 接口并调用方法来使用 LLM。
说到方法,这就是奇迹发生的地方。您将使用自然语言描述您希望 LLM 做什么。首先,您使用 @SystemMessage 定义角色和范围。然后,您可以使用 @UserMessage 描述任务。
@RegisterAiService
public interface TriageService {
@SystemMessage("""
You are working for a bank, processing reviews about
financial products. Triage reviews into positive and
negative ones, responding with a JSON document.
"""
)
@UserMessage("""
Your task is to process the review delimited by ---.
Apply sentiment analysis to the review to determine
if it is positive or negative, considering various languages.
For example:
- `I love your bank, you are the best!` is a 'POSITIVE' review
- `J'adore votre banque` is a 'POSITIVE' review
- `I hate your bank, you are the worst!` is a 'NEGATIVE' review
Respond with a JSON document containing:
- the 'evaluation' key set to 'POSITIVE' if the review is
positive, 'NEGATIVE' otherwise
- the 'message' key set to a message thanking or apologizing
to the customer. These messages must be polite and match the
review's language.
---
{review}
---
""")
TriagedReview triage(String review);
}就是这样!这就是描述 LLM 交互所需的一切。这些指令遵循一套原则来塑造 LLM 的响应。在 专门的提示工程页面 中了解有关这些技术的更多信息。
现在,要从应用程序代码调用 LLM,只需注入 TriageService 并调用 triage 方法即可。
@Path("/review")
public class ReviewResource {
@Inject
TriageService triage;
record Review(String review) {
// User text
}
@POST
public TriagedReview triage(Review review) {
return triage.triage(review.review());
}
}就这样!LLM 现在已集成到应用程序中。TriageService 接口用作调用 LLM 的大使。这种声明式方法具有许多优点:
-
可测试性 - 您可以通过提供接口的伪实现轻松模拟 LLM。
-
可观测性 - 您可以使用 Quarkus 指标注解来监视 LLM 方法。
-
弹性 - 您可以使用 Quarkus 的容错注解来处理故障、超时和其他瞬态问题。
工具和文档加载器
前面的示例有点过于简单。在现实世界中,您需要使用工具和文档存储来扩展 LLM 的知识。@RegisterAiService 注解允许您定义要使用的工具和文档存储。
工具
工具是 LLM 可以调用的方法。
要声明一个工具,只需在 bean 方法上使用 @Tool 注解即可。
@ApplicationScoped
public class CustomerRepository implements PanacheRepository<Customer> {
@Tool("get the customer name for the given customerId")
public String getCustomerName(long id) {
return find("id", id).firstResult().name;
}
}在此示例中,我们使用 Panache 存储库模式访问数据库。我们有一个带有 @Tool 注解的特定方法来检索客户姓名。当 LLM 需要获取客户姓名时,它会指示 Quarkus 调用此方法并接收结果。
显然,将所有操作暴露给 LLM 不是一个好主意。因此,除了 @Tool 之外,您还需要在 @RegisterAiService 注解中列出允许 LLM 调用的工具集。
@RegisterAiService(
tools = { TransactionRepository.class, CustomerRepository.class },
chatMemoryProviderSupplier = RegisterAiService.BeanChatMemoryProviderSupplier.class
)
public interface FraudDetectionAi {
// ...
}chatMemoryProviderSupplier 配置可能会引起疑问。在使用工具时,后台会展开一系列消息。因此,有必要配置 AI 服务的内存以有效跟踪这些交互。chatMemoryProviderSupplier 允许配置内存的处理方式。值 BeanChatMemoryProviderSupplier.class 指示 Quarkus 查找 ChatMemoryProvider bean,如下所示:
@RequestScoped
public class ChatMemoryBean implements ChatMemoryProvider {
Map<Object, ChatMemory> memories = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public ChatMemory get(Object memoryId) {
return memories.computeIfAbsent(memoryId,
id -> MessageWindowChatMemory.builder()
.maxMessages(20)
.id(memoryId)
.build()
);
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
memories.clear();
}
}目前,只有 OpenAI 模型支持工具。
文档存储
文档存储是使用您自己的数据扩展 LLM 知识的一种方式。这种方法 - 称为检索增强生成 (RAG) - 需要两个过程:
- 摄取过程
-
您将文档摄取到文档存储中。文档不是按原样存储的,而是会计算一个嵌入。这个嵌入是文档的向量表示。
- RAG 过程
-
在 Quarkus 应用程序中,您需要声明要使用的文档存储和嵌入。因此,在调用 LLM 之前,它会从存储中检索相关文档(这就是向量表示有用之处)并将其附加到 LLM 上下文(这本质上意味着将检索到的信息从文档添加到用户消息中)。
Quarkus LangChain4j 扩展为这两个过程提供了便利。
以下代码显示了如何将文档摄取到 Redis 文档存储中。
@ApplicationScoped
public class IngestorExample {
/**
* The embedding store (the database).
* The bean is provided by the quarkus-langchain4j-redis extension.
*/
@Inject
RedisEmbeddingStore store;
/**
* The embedding model (how the vector of a document is computed).
* The bean is provided by the LLM (like openai) extension.
*/
@Inject
EmbeddingModel embeddingModel;
public void ingest(List<Document> documents) {
var ingestor = EmbeddingStoreIngestor.builder()
.embeddingStore(store)
.embeddingModel(embeddingModel)
.documentSplitter(recursive(500, 0))
.build();
ingestor.ingest(documents);
}
}然后,通常在另一个应用程序中,您可以使用填充的文档存储来扩展 LLM 的知识。首先,创建一个实现 Retriever<TextSegment> 接口的 bean。
@ApplicationScoped
public class RetrieverExample implements Retriever<TextSegment> {
private final EmbeddingStoreRetriever retriever;
RetrieverExample(RedisEmbeddingStore store, EmbeddingModel model) {
retriever = EmbeddingStoreRetriever.from(store, model, 20);
}
@Override
public List<TextSegment> findRelevant(String s) {
return retriever.findRelevant(s);
}
}然后,将文档存储和检索器添加到 @RegisterAiService 注解中。
@RegisterAiService(
retrieverSupplier = RegisterAiService.BeanRetrieverSupplier.class
)
public interface MyAiService {
// ...
}
RegisterAiService.BeanRetrieverSupplier.class 是一个特殊值,用于在 Quarkus 应用程序中查找 Retriever bean。 |
最后的注意事项
本文介绍了 Quarkus LangChain4j 扩展。这是该扩展的第一个版本,我们将继续探索和实验将 LLM 集成到 Quarkus 应用程序中的方法。我们正在征求反馈和想法以改进这些集成。我们正在努力消除一些粗糙的角落,并探索其他方式来集成 LLM,并在集成 LLM 时带来开发者的快乐。
如果没有 Dmytro Liubarskyi 在 LangChain4j 库上所做的出色工作,这个扩展将不可能实现。我们的合作使我们能够提供一种对 Quarkus 友好的方法来集成该库(包括原生编译支持),并塑造一种将 LLM 集成到 Quarkus 应用程序中的新方式。当前的设计是为了让 Quarkus 应用程序能够轻松使用 LLM。您基本上可以将您的任何 bean 作为工具挂钩,或将数据摄取到存储中。此外,您的任何 bean 现在都可以与 LLM 交互。
我们期待继续这次合作,并看到您将用这个扩展构建什么。

