Mutiny 和 Reactiverse
我被问过很多次:如何在 Quarkus 中使用 Eclipse Vert.x?是的,你可以在 Quarkus 中使用 Vert.x。你可以部署 verticle,使用 event bus 进行通信,或者使用 Vert.x 生态系统中的任何东西。但是,你也可以在 Quarkus 中使用 Vert.x 的 Mutiny 变体,并与其他 Quarkus 提供的响应式 API 获得无缝体验。虽然有几篇文章已经提到了这一点,但它值得一篇专门的博文。那么,我们开始吧。
Eclipse Vert.x
Vert.x 是一个用于构建响应式应用的工具包。Vert.x 的生态系统非常庞大。从 HTTP 和数据访问能力,到通过微服务进行消息传递的客户端和安全设施,Vert.x 的生态系统极其多样化和通用。要了解其多样性,只需查看 Vert.x 文档。这使得 Vert.x 在许多领域都很受欢迎,例如 Web 应用、IoT 网关、银行应用等。
正如你可能知道的,Quarkus 基于 Vert.x。在底层,有一个托管的 Vert.x 实例为 Quarkus 的其余部分提供支持。
当 Quarkus 提供 HTTP 端点时,在底层,有一个 Vert.x HTTP 服务器处理请求和响应。对于消息传递、gRPC 和几乎任何 I/O 操作也是如此。
Vert.x “原生” API 及相关
Vert.x 提供了多种 API。现在我们先关注“原生”API。
遵循 Vert.x 的响应式特性,该 API 主要包含异步方法。这些方法遵循一种语法约定
public void doSomething(param1, param2, Handler<AsyncResult<T>> handler) {
// ...
}有趣的部分是最后一个参数。它是一个函数,更准确地说是一个回调,当操作完成或失败时会被调用。是的,Vert.x 的异步特性不允许使用 try/catch 块。所以你需要传递一个 continuation 回调,该回调会根据操作结果被调用。
AsyncResult 是一个捕获此结果的结构。它包含操作产生的 `<T>` 类型的结果,或者如果操作失败则包含失败信息。
让我们看一个例子
vertx.fileSystem()
.readFile("my-file.txt", ar -> {
if (ar.failed()) {
System.out.println("D'oh! Cannot read the file: " + ar.cause());
} else {
System.out.println("File content is: " + ar.result());
}
});这段代码读取一个文件,由于这是一个异步操作,它会在文件读取完成后调用回调。readFile 方法读取文件的全部内容并将其累积在一个 buffer 中。回调接收异步结果,其中包含文件的内容(ar.result())或失败信息。当操作完成或失败时,Vert.x 会调用此回调。
Vert.x 还通过 ReadStream 和 WriteStream 类支持流。ReadStream 代表你可以读取的数据流。因此,你可以附加一个回调,在流中的每个项遍历时调用。WriteStream 是一个数据源。你可以将项推送到 WriteStream。这些项将被 ReadStream 消费。
vertx.fileSystem()
.open("my-file.txt", new OpenOptions().setRead(true), ar -> {
if (ar.failed()) {
System.out.println(
"D'oh! Cannot read the file: " + ar.cause()
);
} else {
AsyncFile file = ar.result();
// AsyncFile is a read stream, we can read from it:
file
.exceptionHandler(t ->
System.out.println("Failure while reading the file: " + t)
)
// Reads the file chunk by chunk
.handler(buffer ->
System.out.println("Received buffer: " + buffer)
);
}
});| Vert.x 流不实现 Reactive Streams。Vert.x 提供了一种不同的背压协议。 |
为什么这些 API 成型规则很重要?Vert.x 不仅提供一个 API。上面介绍的“原生”API 只是提供的 API 之一。它还提供 Kotlin API、RX Java API 等。
这些 API 是**生成**的。Vert.x 提供了一个代码生成器,可以 _转换_ Vert.x“原生”API 为其他 API。由于所有方法都格式良好,生成器可以理解它们应该如何被适配。
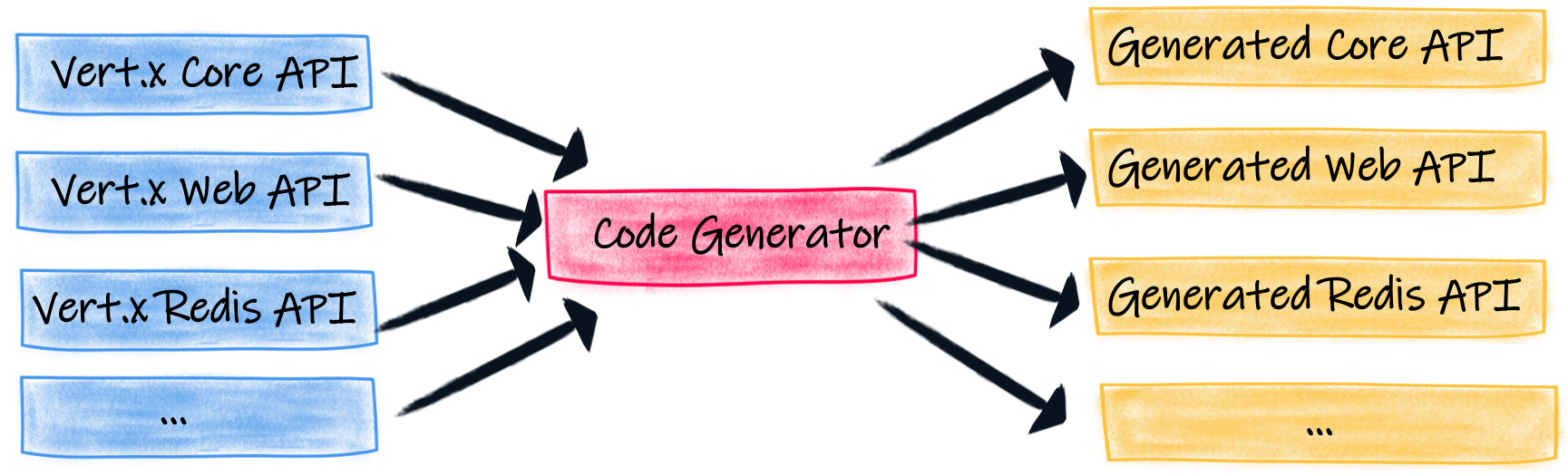
生成的代码暴露了不同的 API;每个方法都委托给“原生”API。异步方法和流可以遵循不同的转换,因此生成的 API 使用了正确的惯用法。
Vert.x Mutiny API
Mutiny 是一个事件驱动的响应式编程库。它与 Vert.x 无关。但是,我们编写了一个代码生成器,可以为 Vert.x API 生成 Mutiny 变体。
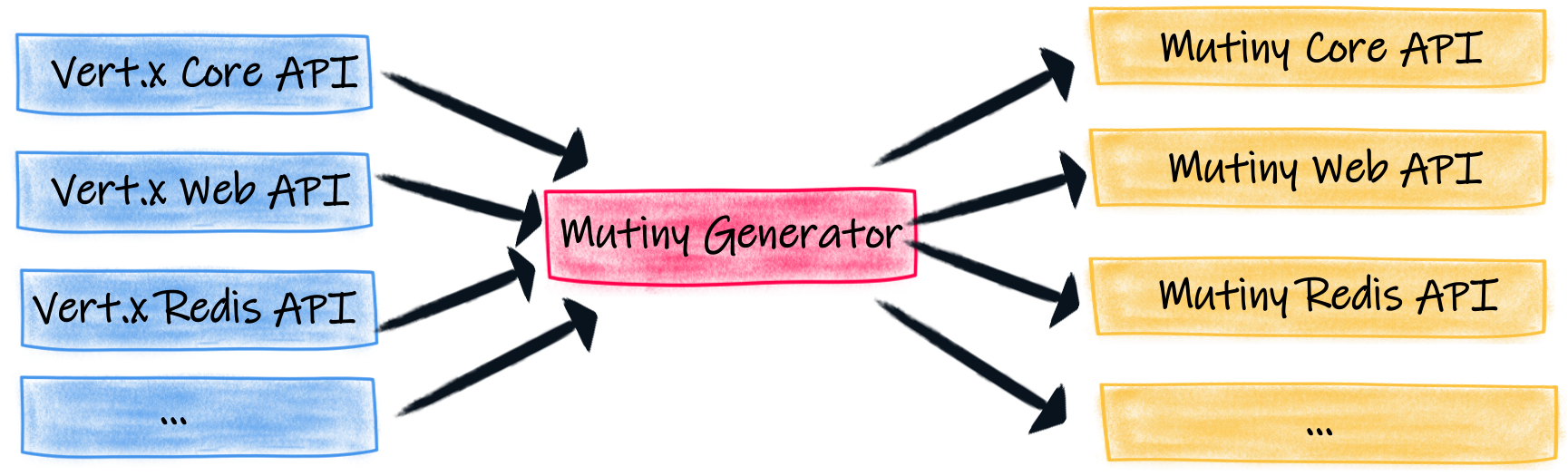
转换是直接的
-
io.vertx包 ⇒io.vertx.mutiny包 -
异步方法 ⇒ 返回
Uni<T>的方法 -
ReadStreams<T>⇒ 可以作为Multi<T>消费 -
WriteStreams<T>⇒ 可以作为 Reactive StreamsSubscriber<T>消费
它还支持 Vert.x 的背压协议到 Reactive Streams,因为 Mutiny 实现了 Reactive Streams。
例如,上面的第一个例子变成了
Uni<Buffer> uni = vertx.fileSystem().readFile("my-file.txt");
uni.subscribe()
.with(it -> System.out.println("File content is: " + it));| 两个 API 之间的一个区别与惰性有关。Vert.x“原生”API 在调用方法后立即触发操作。Mutiny 变体期望订阅来触发操作。 |
上面的流示例变成了
Uni<AsyncFile> uni = vertx.fileSystem()
.open("my-file.txt", new OpenOptions().setRead(true));
uni
// Gets a Multi to read the file:
.onItem().transformToMulti(asyncFile -> asyncFile.toMulti())
// Gets the buffers one by one:
.subscribe().with(
buffer -> System.out.println("Received buffer: " + buffer)
);不止于此
Mutiny 变体不仅应用了上一节中公开的规则。对于异步方法,它还提供了
-
xAndAwait()方法 - 阻塞调用线程直到收到结果。如果发生失败,则抛出RuntimeException -
xAndForget()方法 - 触发操作,丢弃结果
// Read the content of the file in a blocking manner:
Buffer content = vertx.fileSystem().readFileAndAwait("my-file.txt");
// Open and close the file
// Closing the file is an asynchronous operation (returning a Uni).
// We trigger the operation and discard the outcome
vertx.fileSystem().open("my-file.txt", new OpenOptions().setRead(true))
.subscribe().with(file -> file.closeAndForget());在哪里可以找到这个 API?
在撰写本文时,我们仅提供 Vert.x Core 和 Vert.x 客户端(MongoDB、Redis、Web 客户端、Mqtt 等)。我们正在扩展支持以覆盖整个 Vert.x 堆栈。
要使用 Mutiny 客户端,你需要为你的项目添加正确的依赖。浏览 依赖列表 来选择你需要的那个。
例如,要使用 Vert.x Web 客户端的 Mutiny 变体,请添加以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.smallrye.reactive</groupId>
<artifactId>smallrye-mutiny-vertx-web-client</artifactId>
<version>...</version>
</dependency>拥有依赖后,只需创建 Web 客户端实例
@Inject Vertx vertx; // Inject the managed io.vertx.mutiny.core.Vertx instance
private WebClient client;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
client = WebClient.create(vertx, new WebClientOptions()
.setDefaultHost("localhost")
.setDefaultPort(8082)
);
}
private Uni<String> call(String path) {
return client
.get(path).send()
.onItem().transform(HttpResponse::bodyAsString);
}| 缺少什么?在 SmallRye Reactive Utils 上打开一个 issue。 |
| Javadoc 可在此 处 获取。 |

